Wearable Technology In Sports: A Detailed Guide for Coaches & Teams
Reading Time: 12 minutes
Reading Time: 12 minutes
Wearable technology in sports is now a major factor in how athletes prepare, perform and recover. It changes the way teams collect and analyze data, applying their findings to optimize athlete performance.
From fitness trackers worn by recreational runners to advanced communication systems used in professional sports, wearable devices are now part of the daily routines of athletes worldwide.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at how wearable technology has evolved in sports, the different ways teams use it today, and where it’s headed in the future.
We’ll explore the types of devices athletes rely on, the performance metrics they track, how this technology helps prevent injuries, and how innovators like GoRout help teams stay connected and perform at their best.
What is Wearable Technology in Sports?

Wearable technology in sports includes electronic devices athletes can wear to collect, analyze and share data about their physical activity, physiological responses and biomechanical movements.
They can measure speed, heart rate and movement, giving athletes and coaches useful insights for training, recovery, and tracking progress over time.
A wearable device can be a smartwatch, smart clothing, implantable sensors, or electronic fabrics. All of these are designed to monitor and improve how athletes perform.
In professional sports, these devices also make it easier for coaches and players to communicate during games and training, helping improve performance, strategy, and decision-making.
Historical context
The story of sports wearable technology starts with simple pedometers that count steps. These early devices were limited in scope but showed the potential of tracking physical activity.
By the 1980s and 1990s, heart rate monitors became popular, giving athletes and coaches a way to measure training intensity.
In the early 2000s, GPS trackers and accelerometers entered professional sports. Professional athletes were the first to use these technologies to monitor performance metrics such as speed, distance and movement patterns during training and competition.
Soccer clubs, rugby teams and American football organizations started using them to measure distance covered, sprint counts and workload.
Over time, these devices have become smaller and more accurate. Their price has also decreased, making them more affordable for all levels of play.
Today, wearable tech includes everything from smart clothing and GPS trackers to augmented reality glasses and AI-powered performance analysis tools.
Current state
Wearable technology is now a regular part of professional sports training. Athletes use GPS vests to track movement, basketball players wear motion sensors to study their jumps, and swimmers rely on smart goggles to measure stroke efficiency.
These tools give athletes detailed feedback on how they train and recover, making it easier to improve performance.
Even at the amateur level, fitness trackers and personal devices like the Apple Watch have made advanced monitoring accessible to millions of recreational athletes.
Key stakeholders
The adoption of wearable technology involves multiple groups:
- Athletes use wearables to monitor training intensity, recovery, athletic performance, and other health-related data.
- Coaches use the data to design training programs and adjust strategy in real-time.
- Sports scientists interpret performance data to guide performance optimization.
- Medical staff use wearables for injury prevention and rehabilitation in sports medicine.
- Sports organizations invest in emerging technologies to stay competitive in the global sports industry.
All of these groups work together to make wearable technology useful for improving performance, protecting health, and keeping teams competitive.
What Are the Types of Wearable Devices in Sports?
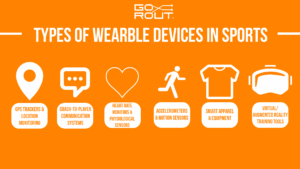
Wearable technology in sports can be integrated into different training methods to optimize intensity, recovery and players’ technique.
Each type of device gives coaches and athletes unique insights that shape how they train and compete.
GPS trackers and location monitoring
GPS trackers are some of the most common wearables in professional sports. They record distance covered, sprint counts, and player positioning.
These devices also track movement patterns, giving coaches detailed data on workload and biomechanics.
With all this info, teams can better manage training loads and avoid overtraining while keeping up with the physical demands of competition.
Coach-to-player communication systems
Good communication can impact the outcome of a game. Every second matters, and confusion can cost a team valuable opportunities.
Instead of relying on hand signals, shouted instructions, or paper play sheets, coaches can now send plays directly to athletes through GoRout’s wearable systems.
This ensures players always know the call, reduces mistakes, and helps teams stay one step ahead of their opponents.
GoRout Scout and Gridiron (football)

GoRout Scout is built for practices, while Gridiron is designed for games. Both use coaches web and mobile apps and digital wristbands worn by players.
Coaches load plays into the web system, and with the push of a button on the mobile app, the play call instantly appears on players’ wristbands.
It eliminates wasted time huddling, shouting, or signaling from the sideline. Players get the call instantly, line up, and execute.
Benefits:
- Faster practices: Coaches can run more reps in less time because plays are delivered instantly.
- Clear communication: Every player sees the exact same call on their football play call wristband, reducing errors and confusion.
- Game-day advantage: Gridiron allows teams to adjust on the fly, even in loud stadiums where verbal communication is impossible.
- Confidence boost: Players don’t have to second-guess the play call. They know exactly what’s expected.
Want to speed up your practices and sharpen your game-day execution? Get a quote for GoRout Scout and Gridiron and see how they can transform your football program.
GoRout Diamond (baseball & softball)

GoRout Diamond is designed for baseball and softball teams. Instead of relying on hand signals—which opponents can easily steal—coaches send pitch calls, defensive alignments, or base running instructions directly to players’ baseball play wristbands.
The system is encrypted, meaning all communication stays private. Players receive the call instantly, so there’s no delay between the coach’s decision and the team’s execution.
Benefits:
- Stops sign stealing: Calls are delivered securely, keeping opponents from gaining an advantage.
- Keeps players focused: Athletes no longer have to look to the dugout for signals. They can stay locked into the game.
- Faster pace of play: Games move more smoothly when communication is instant.
- Flexible strategy: Coaches can change defensive shifts or pitch sequences in real time without confusion.
Ready to protect your signals and give your team a competitive edge?
Get a quote or visit the web shop.
Heart rate monitors and physiological sensors
Heart rate monitors and sensors track how the body responds to training.
They measure heart rate, heart rate variability, and body temperature to show how hard athletes are pushing themselves and how well they are recovering.
Coaches analyze this data to identify fatigue or overtraining and adjust workloads to prevent injuries.
Accelerometers and motion sensors
These wearables monitor speed, direction, and impact.
- In basketball, they track jump metrics
- In football, they analyze collisions
- In baseball, they measure throwing mechanics
Sports scientists also use motion sensors to study movement patterns, giving teams valuable data to improve performance and reduce injury risks.
Smart apparel and equipment
Smart clothing and shoes have sensors built right into the fabric or footwear. A smart shirt can track breathing and muscle activity, while smart shoes can measure stride length and ground contact time.
These tools give athletes continuous feedback without interfering with performance.
Virtual/augmented reality training tools
Virtual and augmented reality tools let athletes practice game situations in a realistic but controlled environment. Smart glasses can show tactical info, while VR platforms offer really immersive training experiences.
These tools are especially helpful for developing skills, improving reaction times, and rehearsing strategies.
What are the Key Performance Metrics Tracked by Wearables?
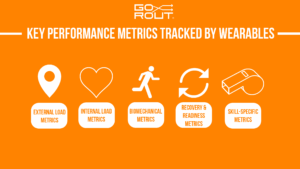
One of the biggest benefits of wearable tech is that it can track performance metrics and give a clear picture of an athlete’s workload, recovery, and skills.
External load metrics
External load shows the physical work an athlete does. GPS trackers and accelerometers measure distance, sprints, and accelerations.
For example, a soccer player might run 10 km in a game, with 1 km at high speed. It helps coaches balance training and avoid overwork.
Internal load metrics
It shows how the body responds to training. Heart rate monitors track average and max heart rate, while HRV (heart rate variability) shows recovery status.
Tools like TRIMP and RPE combine numbers and athlete feedback to give coaches a complete view of performance.
Biomechanical metrics
Biomechanical data looks at movement efficiency. Motion sensors measure stride length, ground contact time, and joint angles.
In baseball, this can reveal throwing issues that may cause injuries. In running, it can highlight inefficiencies that slow athletes down.
Recovery and readiness metrics
Sleep monitors give info on the rest quality and duration, while HRV and soreness levels help coaches figure out if athletes are ready for high-intensity sessions.
Skill-specific metrics
These focus on technical skills. In baseball, sensors track bat speed and swing mechanics. In swimming, wearables measure stroke rate and turns. In basketball, they analyze reaction time and decision-making to sharpen performance.
What are the Specific Applications of Wearables in Sports?

Different sports have unique physical and tactical demands, and wearable technology provides solutions for each discipline.
American football
American football is a rough-and-tumble game that needs a lot of communication. Helmets have sensors that track impacts, while GPS trackers keep tabs on speed and player positions.
GoRout’s football play-calling system has changed communication, allowing coaches to send plays instantly and securely. It ensures athletes receive instructions without confusion, even in noisy stadiums.
Baseball and softball
Baseball and softball players can really gain from using wearable sensors that keep an eye on how they swing, pitch, and recover after games.
GoRout’s baseball pitch-calling system provides secure communication between pitchers and catchers, eliminating the risk of sign stealing.
These tools help optimize batting mechanics, pitch design and defensive strategies.
Soccer
In soccer, GPS trackers measure distance covered, sprint counts and tactical positioning. Coaches use this data to analyze formation strategies and pressing intensity.
Smart balls with embedded sensors provide additional insights into passing accuracy and shot power. Video analysis tools integrate with wearables to provide a full picture of team performance.
Basketball
Basketball players use accelerometers and motion sensors to track jump counts, acceleration patterns and fatigue levels.
Shot-tracking technology provides detailed information about shooting mechanics, allowing players to refine their technique.
Coaches use this data to monitor training and prevent overtraining-related injuries.
Swimming
Swimming is unique because athletes train in water. Devices like FORM Smart Swim Goggles and TritonWear track stroke rate, split times and underwater mechanics.
Coaches use this data to analyze turn efficiency and drag profiles, helping swimmers optimize performance in competition.
What are the Benefits of Wearable Technology in Sports?
The benefits of wearable technology in sports go beyond data collection. They change how athletes prepare, compete and recover.
- Talent identification: Helps coaches spot promising athletes earlier by tracking natural sports performance patterns.
- Return-to-play confidence: Provides objective data that reassures athletes and coaches when it’s safe to come back from injury.
- Nutritional insights: Paired with other tools, wearables can show how hydration or diet impacts performance and recovery.
- Mental load tracking: Emerging wearables monitor stress levels to support mental health alongside physical performance.
- Benchmarking across teams: Allows organizations to compare performance data across squads, age groups, or training cycles.
- Customization at scale: Makes it possible to tailor training for large groups of athletes while still accounting for individual needs.
- Recruitment advantage: Data-backed performance history can strengthen an athlete’s profile when being scouted.
- Environmental adaptation: Some wearables track how athletes perform in different conditions (heat, altitude, humidity) to adjust preparation.
- Sponsorship and commercial value: Wearable data can be packaged into insights for sponsors, creating new revenue opportunities.
Together, these benefits show how wearable technology goes beyond performance tracking to create value for athletes, teams, and the wider sports industry.
“I’ll use GoRout no matter where I coach for the rest of my career. It’s phenomenal!” – Coach Brian Lowery, Eastern View High School Football (2024)
What are Injury Prevention and Recovery Applications?
Wearable technology is not only about tracking performance. It also plays a growing role in keeping athletes healthy and helping them recover faster. Beyond monitoring workloads and sleep, new applications are pushing the boundaries of sports medicine.
- Early detection of muscle fatigue: Advanced sensors can pick up subtle changes in muscle vibration or activation, signaling fatigue before an athlete feels it. It allows coaches to adjust training loads before injuries happen.
- Real-time impact monitoring: In contact sports, helmet and body sensors record the force and frequency of impacts, helping medical staff spot potential concussions or overuse risks immediately.
- Rehabilitation progress tracking: During recovery, wearables measure range of motion, strength, and stability, giving therapists concrete data to guide rehab programs and track milestones.
- Personalized warm-up routines: Data from wearables can suggest tailored warm-ups that target weak areas or muscle imbalances, lowering the chance of strain or re-injury.
- Hydration and heat stress monitoring: Some devices now track sweat composition and body temperature, helping prevent heat-related illnesses and ensuring athletes stay properly hydrated.
- Post-injury confidence building: Wearables provide athletes with proof of progress — such as improved joint stability or reduced asymmetry — which can reduce fear and hesitation when returning to play.
- Remote rehabilitation support: Athletes recovering away from team facilities can use wearables to share progress with medical staff in real time, ensuring consistent oversight no matter where they are.
Injury prevention and recovery applications show how wearable technology is moving from simply tracking performance to actively protecting athletes and supporting long-term health.
Implementing Wearable Technology in Sports
To get real value from wearable tech, you need a plan. Following best practices helps you collect accurate data, make sense of it and use it in a way that benefits athletes.
- Needs assessment: Start by identifying what performance metrics are most important for your sport. For example, a football team may focus on distance and sprint counts, and a baseball team may focus on throwing mechanics and reaction time.
- Data collection protocols: Collect data in the same way during training and games. This way, results are reliable and comparable over time, not just random snapshots.
- Interpretation frameworks: Raw data is overwhelming. Use clear systems to turn complex numbers into simple, actionable insights for training and recovery.
- Athlete education: The team should know what data is being collected, why and how it benefits them. When players see the value, they are more likely to engage with the tech.
- Integration: Wearable data is most powerful when combined with other tools, like video analysis, medical evaluations and athlete feedback, to get a complete picture of performance and well-being.
When used correctly, these best practices make wearable tech a reliable tool for better coaching and improved results.
What are the Challenges with Wearable Technology in Sports?
While wearables are great, they also bring challenges for athletes, coaches and organizations.
Data privacy
One of the biggest is data privacy. Performance data from wearables is personal data. Who owns it, and how should it be used?
Athletes will worry about their data being shared without consent, while sports organizations need to have clear policies in place to protect privacy.
Technology reliability
Not all devices are created equal, and accuracy can vary greatly. If wearable sensors produce bad data, coaches will make poor decisions based on flawed info.
Technology reliability is key to building trust in these systems.
Information overload
Wearables generate a ton of performance data. Without proper frameworks to interpret the data, coaches and athletes will be overwhelmed.
The challenge is to filter out the noise and focus on the actionable insights that actually improve performance.
Cost barriers
High-end wearable performance devices are expensive, creating accessibility issues for youth teams, smaller clubs and developing sports.
As the technology gets better, costs will come down, but for now, price may be a barrier.
Over reliance risks
Finally, there is the risk of overreliance on technology. While wearables provide great data, they should complement – not replace – coaching intuition and an athlete’s self-awareness.
Balancing human expertise with technological insights is key to long-term success.
What’s Next for Wearable Technology in Sports?
Wearable technology will get even smarter and more integrated.
Biometric monitoring
Wearables will soon track glucose levels, hydration status and electrolyte balance in real-time. Athletes will be able to manage nutrition and recovery better.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning
AI will enable predictive analytics for injury prevention, automated play-calling and personalized training. Coaches will make faster and better decisions.
Miniaturization and integration
Future wearables will be smaller, lighter and more integrated into athletic gear. Microchips will be embedded in uniforms, protective gear, or personal devices, such as smart jewelry.
Battery life will improve so teams can use wearables daily without recharging. Coaches and athletes will collect data without disrupting training or competition.
Augmented coaching
Coaching will also evolve with augmented reality and wearable communication systems.
Smart glasses will project tactical information into an athlete’s line of sight, and AR visualizations will help coaches illustrate plays in real-time.
As augmented coaching tools get more advanced, they will enhance performance monitoring and play-calling even more.
Conclusion on Wearable Technology in Sports
Wearable technology has changed the way athletes train, compete and recover.
From GPS trackers that monitor movement patterns to communication systems that improve team performance, these devices provide valuable data to support performance optimization and injury prevention.
As emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, smart clothing, and augmented coaching develop, wearable tech will become more integrated into the sports industry.
Ultimately, the future of wearable technology in sports is about balance — using data to improve performance while keeping athletes healthy, motivated and focused on the game.
Companies like GoRout are leading the way by developing innovative wearables that improve communication and ensure athletes get instructions instantly and securely.
Get a quote today to see how it fits your team.
Frequently Asked Questions on Wearable Technology in Sports
What are the wearable technologies in sport?
Wearable technologies in sport include GPS trackers, smart clothing, fitness trackers, communication systems, smart shoes and augmented reality tools.
What are the four wearable technologies?
The four main categories are smartwatches, smart clothing, smart glasses, and smart jewelry.
What is the impact of wearing wearable tech in sports?
It allows athletes and coaches to collect data, analyze performance and make informed decisions that support performance enhancement and injury prevention.
What is wearable technology in the NFL?
In the NFL, wearable devices such as GPS trackers, helmet sensors and GoRout communication systems are used for athlete monitoring, performance optimization, and tactical decision-making.
What are the most popular wearable devices used by athletes today?
The most common devices are the Apple Watch, GPS trackers, fitness trackers, smart shoes and GoRout’s digital wristbands for secure communication.
How are wearable tech innovations changing team strategies?
They give coaches objective performance data, tactical insights, and communication tools to adjust strategy in real-time.
How do wearables prevent injuries in professional sports?
By monitoring training intensity, movement patterns and recovery readiness, wearables detect early signs of overtraining and reduce injury risk.
How are wearables changing athlete training and recovery?
They provide continuous monitoring of sleep patterns, workload and biomechanics so coaches and medical staff can design effective training programs and recovery protocols.